 U.S. naval ship vendors could learn a thing or two from the French, as they’ve thusfar fought off extensive American efforts to intrude on France’s niche market in small surface combatants.
U.S. naval ship vendors could learn a thing or two from the French, as they’ve thusfar fought off extensive American efforts to intrude on France’s niche market in small surface combatants.
It’s almost embarrassing. Despite American efforts to sell the Littoral Combat Ship, the French Gowind-Class corvette “family of ships” has quietly taken big bites out of the LCS’s international market. With the Gowind ships, France has simply out-hustled the LCS program, picking up two big orders from Malaysia and Egypt–and DCNS is actively looking to seize other key markets.
The United States should take a good long look at France’s Gowind program, and ask why the French have been so successful.
If you’re not familiar with the L’Adroit and the Gowind Class, as patrol craft go, the DCNS-built Gowind Class is pretty simple. It is an EEZ patrol craft, that, in the platform’s simplest variant, focuses on the basics–being an economical and seaworthy platform for ISR and small law enforcement/special operations activities. The Gowind Corvette program offers more complex variants, but the first-in-class built-on-spec platform is the base “no-frills” model. Built by DCNS, the first platform, the L’Adroit, was effectively “loaned” to the French Navy in 2011 for three years of assessments and marketing.
Here is why the A’droit is making sales:
 France Knows–And Accepts–The Patrol Mission: The first reason that France is carrying the low-end in the littorals is because they’ve focused on that mission. Boasting one of the world’s largest–and one of the most widely distributed–Exclusive Economic Zones, France has been doing the maritime EEZ patrol “beat” for a long, long time (some of my prior discussions of France’s maritime territories are here and here). Even if France’s patrol ships aren’t “survivable”, the French know what they are doing, they have a good strategy that uses low-end ships as tripwires, and, as far as the low-end patrol combatants go, they’ve kept their ships deliberately simple and seaworthy.
France Knows–And Accepts–The Patrol Mission: The first reason that France is carrying the low-end in the littorals is because they’ve focused on that mission. Boasting one of the world’s largest–and one of the most widely distributed–Exclusive Economic Zones, France has been doing the maritime EEZ patrol “beat” for a long, long time (some of my prior discussions of France’s maritime territories are here and here). Even if France’s patrol ships aren’t “survivable”, the French know what they are doing, they have a good strategy that uses low-end ships as tripwires, and, as far as the low-end patrol combatants go, they’ve kept their ships deliberately simple and seaworthy.
Earlier patrol craft like the Floreal Class Surveillance Ships are great because they’re nothing special–they boast a gun, some anti-ship missiles, a helicopter, quarters for special operators and some negligible anti-aircraft capabilities, these slow diesel-powered civil-spec wonders sail like corks and travel all over the world. They’re perfect for what they do, and France, I think, knows that. (Not that there haven’t been failures–the La Fayette Class, France’s flirtation with a higher-end patrol combatant, has had something of a rocky service record with foreign customers.)
But, at the end of the day, there was (and is) no institutional bickering about the vessel–the L’Adroit was a non-threatening offering, slotting right into into a CONOPS that was already developed and ready, while the LCS rode headfirst into a self-defeating doctrinal storm. And, with L’Adroit being on a temporary loan, any institutional concerns over “unusual” practices could be dismissed as L’Adroit was merely and “experimental” platform.
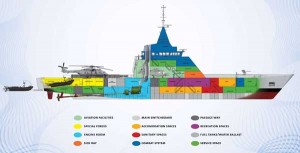
 DCNS Kept It Simple: The L’Adroit, a prototype “on loan” to the French Navy, is simple. There is nothing on the thing but a sea-frame and electronics. It’s just a ship with potential–and rather than being distracted with combat tasks, the commander and crew were free to focus on maximizing the reliability and potential utility of their modest vessel. Rather than wrestle with lots of weapons and modular systems and modules and everything else, DCNS kept it simple–quickly integrating a UAV, demonstrating seaworthiness and robustness. Here’s the mission set:
DCNS Kept It Simple: The L’Adroit, a prototype “on loan” to the French Navy, is simple. There is nothing on the thing but a sea-frame and electronics. It’s just a ship with potential–and rather than being distracted with combat tasks, the commander and crew were free to focus on maximizing the reliability and potential utility of their modest vessel. Rather than wrestle with lots of weapons and modular systems and modules and everything else, DCNS kept it simple–quickly integrating a UAV, demonstrating seaworthiness and robustness. Here’s the mission set:
With two French Navy crews rotating every four months, L’Adroit will offer a high level of at-sea availability, spending 220 days a year on operational missions.
Over the next three years, the French Navy will be thoroughly testing the new ship and its advanced equipment and systems: UAV, commando boat launch ramps, panoramic bridge and single enclosed mast for 360° visibility, teleconferencing facilities, long-range acoustic devices, etc. With these high-tech systems, the ship is ideally equipped for current and emerging maritime safety & security missions, including fisheries surveillance, counter-piracy, drug interdiction, environmental protection, humanitarian aid, and search & rescue.
Basic stuff. LCS became a pawn in a large and complex battle over over “systems-of-systems” and about what company might gain an entrance into the U.S. Navy’s combat systems market, and, despite the rhetoric about starting simple (Flight Zero?) the program bit off a lot more than it could realistically chew.
 DCNS Moved Fast And Structured the Procurement Correctly: DCNS designed and built the L’Adroit in less than 24 months–France meant to beat LCS to the field, and, by god, they did.
DCNS Moved Fast And Structured the Procurement Correctly: DCNS designed and built the L’Adroit in less than 24 months–France meant to beat LCS to the field, and, by god, they did.
By building the ship “on spec”, DCNS had the appropriate incentive to “get it right first”–and then, by retaining ownership, it was far easier for DCNS to cover the few things that didn’t go so well.
My opinion is that the speculative nature of the L’Adroit venture paid enormous dividends. Far too many in the U.S. naval shipbuilding community adhere to a model that can be articulated in a single sentence:
“They’re going to pay us to build it and then they’re going to pay us even more to fix it later.”
With that kind of attitude, you get first-in-class ships that don’t work. A spec boat has to work. Rather than grin as obvious mistakes in government build-specs are inculcated into the design, shipbuilders working on a speculative platform are appropriately incentivized to get stuff right.
There’s just too much at stake to fail. And DCNS certainly didn’t fall flat–even though everything else around the production side of the house (first in class, first patrol boat for yard, etc) suggested the ship was going to be a disaster.
 The Marketing Was Done Right: If the primary purpose of the ship is that it be sold to other countries, it is easier to build a ship that isn’t burdened by persnickety requirements, testing irritants and so forth. Put another way, if the builder defines the requirements, the ship will (shockingly!) be a smashing success every single time.
The Marketing Was Done Right: If the primary purpose of the ship is that it be sold to other countries, it is easier to build a ship that isn’t burdened by persnickety requirements, testing irritants and so forth. Put another way, if the builder defines the requirements, the ship will (shockingly!) be a smashing success every single time.
As a marketer, it’s so much easier to show up with a ship and ask the user “What can you do with it?” To contrast, American procurement is too hung up on regulatory minutiae–and then the test and trials community spends waaay too much time asking (after the bloody platform is built, no less!) “Does this meet my requirement?” (and then they go and compound the problem by engaging in self-affirming chest thumping upon discovery of infractions). The American test-and-trials process rips ships apart–and while that may be a good thing for the sailors, it sucks for overseas marketing of new platforms.
 France Government Supports International Marketing: Compared to France, the U.S government really struggles to sell new naval ships. It’s something of a lost art.
France Government Supports International Marketing: Compared to France, the U.S government really struggles to sell new naval ships. It’s something of a lost art.
Aside from France’s subsidies to their shipbuilding industry, and aside from America’s reputation-bruising process of getting new ships into service, it is very difficult for American shipbuilders (particularly the small ones) to actually get in front of foreign customers.
First, shipbuilders need to plod through the country-specific licensing and marketing authorizations required to actually go to market. If you don’t get a license to market in country X or Y, you can’t market.
The licensing process itself is a long and bureaucratic mess. There are too many different constituencies that need to be appeased (and who pride themselves in–my opinion–on running their own little independent and unmanaged economic and policy shops) to allow for a swashbuckling “let’s pursue any lead” approach to ship marketing. If the primary ship vendor doesn’t have months of lead-time, the project won’t be authorized. It is my sense that France leans far further forward, and commits the whole of government to support foreign ship sales (of course, one might use the excesses involved in selling the La Fayette Class to suggest that France can lean a little too far forward…).
Then there is the sale itself. With the American Foreign Military Sales process, the vendor isn’t selling the ship–the U.S. Government is selling the ship–which makes for a convoluted, time-consuming experience even in the best of circumstances. And rather than simply focus on the ship itself–and making the sale–the U.S. FMS process gets far too distracted by going and including things like sustainment and training and injecting (lots and lot) of ancillary equipment into the mix. That’s all valuable (and it can add billions to the overall sale price), but, still it’s a needless distraction from, well, making the sale (and sometimes it totally antagonizes the potential buyer, too).
Ship FMS deals need to focus on the ship. Make the sale and the rest can come later. That is, at least, my sense of how France has approached ship sales in the past.
And then there’s just general encouragement. The American Navy’s Foreign Sales Office is a relatively sedate place populated by lots of folks on their way out of the Navy. On the other hand, in France, there seems to be far more energy and commitment to selling ships overseas. Take the Gowind manning scheme–the L’Adroit was built on spec, and then, essentially, given to the French Navy for three years of marketing duty testing. The U.S. Navy, today, would never agree to such a scheme–you’re stuck with marketing an “in-service” combatant, but, without high-level help, they’re not going to make it easy for the builder. It’s hard enough to eke out an idea of where a U.S. combatant might be from one day to the next, let alone trying to educate key sailors and coordinate a marketing-oriented visit for the platform. And that, I think, is a shame–because a current, in-uniform user/operator is far more effective as a marketer than even a recently-separated veteran.
Again, I think the L’Adroit experiment paid off by forcing the Navy to work hand-in-hand with DCNS. And while the collaboration must have been quite a challenge, with the Navy personnel probably confronting some real difficulty in preparing the ship for both operations and marketing work, the officers and sailors on board now have a much stronger understanding of what is needed to “make the sale”. After developing a cadre of in-uniform ship salesmen, it’s going to make France that much more effective in selling other vessels.
America–and the American Navy–needs to come to terms with the fact that the country can’t sell new combatants well.
That’s a shame, because everybody in the Navy would love to see American shipbuilders get more business. So. To make the U.S. a more competitive marketplace for naval ships, I humbly suggest the Navy study the L’Adroit case and work to:
1. Calm the arms sales bureaucracy or take steps to reform some of the more onerous bureaucratic requirements. It would be great if the Department of Defense and State could make the initial marketing approval process easier–maybe by offering a uniform “global” marketing approval scheme (authorizing marketing in a blanket list of countries), so shipbuilders need only apply for initial marketing approval once or twice.
2. Realize that aircraft marketing (which the U.S. does very, very well) is very, very different from ship marketing.
3. The Navy needs to decide if selling ships is a strategic priority. If so, then, the Navy needs to work to build “all-of-government” support for such ventures.
4. Support prototype and market-development platforms. I’d love to see some of these small and hungry yards (Bollinger? Dare ya!) build a spec combatant that fits into one of the “1000-Ship Navy” sweet spots. Let’s develop a naval cadre (future FAOs?) to man and market prototypes that encourages the shipbuilding sector to take L’Adroit-like risks–and if future Navy ships came from these prototypes (hey, look, a US-built conventional sub!), then we’d have already worked through a lot of the issues and concerns BEFORE they became a program of record.
5. Frankly, I’d encourage an all-out effort to introduce theatre-wide, uniform “NATO-like” standard designs to the Pacific. Let’s start with the small Pacific Patrol Boat initiative, and go from there–I’d love to see Canada, Japan, Australia, South Korea and the US come together (in whatever ad-hoc group that can) to develop low-end designs for naval tugs, rescue and salvage, replenishment, ice-breaking and patrol craft. Such an initiative would drive strategy discussions, lower costs and make Pacific operations so much easier.
America should be selling Navy ships right and left. But a lack of vision and imagination is killing us at the marketplace, and, until something changes, we’ll cede the market to cheap, simple ships from energetic, hungry and well-supported ship sellers from France, China, Spain and beyond.


{ 1 trackback }
{ 7 comments… read them below or add one }
Egypt just ordered (6) Gowind Corvettes from France. This business should have been directed to a USA shipyard instead of France. We seems to be very talented in driving away our allies, our customers and in losing business to other countries.
DaveH–
Hungry companies build on spec all the time. Heck, drones (as we know them today) wouldn’t have existed if some companies took risks and built on spec. General Atomics is still building neat stuff on spec. So, while you and I both can point to cases where companies took risks and failed, let’s not forget that there are quite a few out there who succeed–that we don’t hear about.
I think you ARE right in that it’s extremely risky–maybe even stupid–to try and rely on a spec program to dethrone an established niche. It’s hard enough to develop something new for an entirely open niche–but for established programs or products, incumbents can easily fight off more efficient or lower-cost insurgents…
Anyway. Food for thought.
Remember when Northrupt built a 100% company funded, upgraded version of the F-5 aircraft……… the F-20 Tigershark??
( The Northrop F-20 Tigershark (initially F-5G) was a privately financed light fighter, designed and built by Northrop. Its development began in 1975 as a further evolution of Northrop’s F-5E Tiger II, featuring a new engine that greatly improved overall performance, and a modern avionics suite including a powerful and flexible radar. Compared with the F-5E, the F-20 was much faster, gained beyond-visual-range air-to-air capability, and had a full suite of air-to-ground modes capable of firing most U.S. weapons. With these improved capabilities, the F-20 became competitive with contemporary fighter designs such as the General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon, but was much less expensive to purchase and operate.)
A GREAT inexpensive aircraft ……….. (Mach 2 capability) which wasn’t designed by the Air Force, and was strangled in it’s crib. Because the U.S. Air Force wouldn’t touch it, no foreign nation wanted it either.
That was probably the very last time a U.S. company will stick it’s head out and try something innovative in weapons development. The U.S.shipbuilding industry would rather eat the crumbs of industry than than risk their companies on something new and innovative.
American De-Industrialization
Continues Unabated
I think there are a few barriers to brining French designs into the US for service in the fleet–just my opinion. It would be interesting to see what went wrong with the VT Halter’s Gowind variant offering for the Offshore Patrol Cutter–if the team got dinged for design issues or something else…
P.S. This is the latest French take on LCS… for the future Polish surface combattant.
Notice how a pair of these Gowind corvettes can probably can do as much as LCS (if not more? Superior range, accommodation & armament on only 1,500 tons), without any of the fancy trimmings.
http://www.planobrazil.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/Gowind-3.jpg
http://www.planobrazil.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/Gowind-1.jpg
http://www.navyrecognition.com/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=1894
“To sell U.S. Combatants Overseas”… why stop there? The French approach also has a ton of lessons for the future SSC:
* Simple steel hulls with lots of growth margin.
* Diesel propulsion.
* Extra accommodation
* Plenty of range
* Passive survivability & stealth built-in, leading to larger than “normal” hulls
(which is fine because they don’t have a self-defeating obsession with artificial tonnage limits… 6,000 ton frigate anyone?).
* No obsession with squeezing the maximum “lethality” or speed into their second-tier combattants… i.e. a focus on balanced design.
If the Navy’s SSC committee is intellectually honest, they should recognize that simply going for an up-armed, more lethal LCS Flight II won’t solve LCS’s basic platform issues. The above features are not the kind that can easily be retrofitted into an existing hull design… especially one that only offers 1.5% service growth margin to play with.